The goal of this case study is to show you how removing low-value pages from your site and the Google index can benefit your website.
Pages removal may have a disruptive effect on your site. If you choose to follow this process, you should understand the rationale behind each step and only implement changes if you have a deep knowledge of the website, SEO expertise and adequate resources.
The following case study is part of an overall SEO Audit and is the cornerstone of the SEO strategy.
During the content audit, a number of blog posts looked as if they did not bring any traffic, backlinks, conversions and little traction in social media. However, they helped to bring in new (offline) business partnerships with other companies, and so they had to be technically handled separately.
Page quality is a hot topic right now; this is because it is hard to define what quality content is. Is quality important to rank? Or to help a potential customer? Or to define your business? All of these questions need to be considered when hiring an agency or a consultant to create content.
It is possible that a website can rank highly without converting readers into leads or have high converting pages with low traffic. Often the top 10 pages are responsible for most of the traffic, and sometimes conversions.

Tasks Prioritization
The onboarding process is important with new clients. Prior website analysis, understanding the client (and their customers), resources, site performance, the competition, and the market, and goals define strategy. Usually, at this point, a list of implementable steps is given to clients, but it is also important to help them to prioritize.
Case Study: A Slash Horror Show
A website with no previous SEO input. 99.97% of low-value website content needed to be eliminated.
The client had a double goal:
- Improving brand awareness against competitors.
- Increasing organic conversions (currently mainly via PPC).
The business sells historical reports for a category of used products. They run database queries and provide free reports. With the paid version, customers are provided all the information required to buy the best product.
Superficially the website looked successful. Further analysis revealed that it only ranked for a small set of keywords, within a narrow topic.
The several technical issues were prioritized into five urgent problems:
- Mixed http & https protocols, with www and non-www pages.
- A loop of redirects due to multiple site re-designs.
- Incorrect Canonical tags implementations.
- Thousands of Tag pages.
- Poor quality duplicate content representing the more than 90% of the page.
Mixed protocols, redirects and incorrect Canonicals were resolved within weeks.
To fix the duplicate tag pages, the same method was utilized as the other millions of URLs.
The duplication issue was because there was a page for every product (one for each brand/model and also for each product code) as they misguidedly thought this would help them rank on Google. They also had a large four-year archive of hundreds of daily on-site searches. But each free report contained very little information and in many cases, the difference between them was less than 10 words (reports averaged 50 words in total).
Analysis of the previous 12-month activity revealed the top 20 landing pages were responsible for more than 85% of the organic sales and 60% of the traffic. In contrast, the free reports contributed to less than 4% of the conversions, and less than 8% of the traffic.
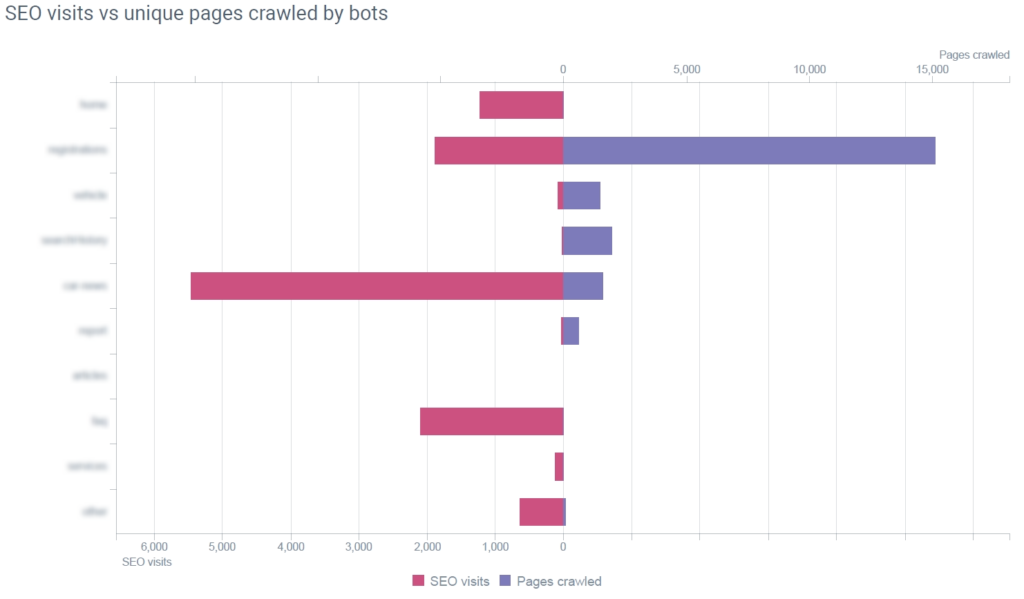
In fact, they were making Google crawl (and spend resources) on millions of low-value, auto-generated pages rather than the user-oriented pages.
The following report from OnCrawl clearly show the relationship pageviews vs. page crawled by bots:
A Supportive Team
The duplicate pages needed to be deleted from the website, as well as the Google index. Because of prior affection for the pages and business model, it was not going to be easy to convince the client of this.
However, the results achieved during the initial fixing period assured the supervisors that this was the correct plan of action.
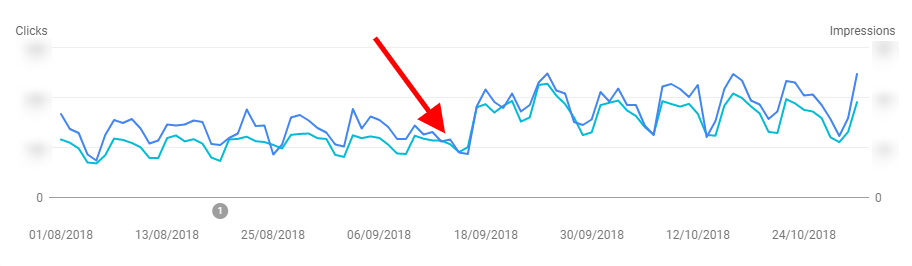
Through the initial impact of work undertaken, I was able to win the confidence of the management and the support of the dev team.
SEO Pruning At Scale
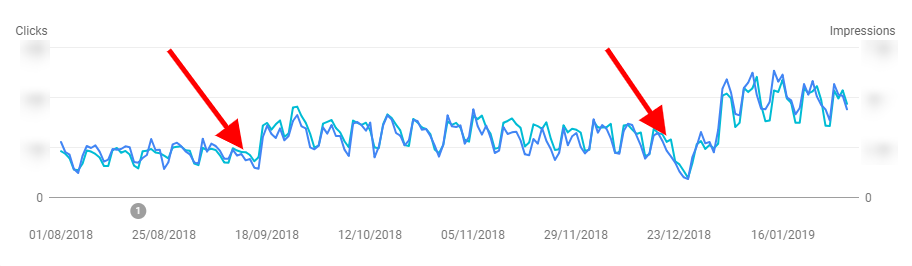
SEO Pruning can often result in working on different scales. In this case, 99.97% of the pages were removed leaving only 1200.
Removal of unnecessary content helps to save resources (time, technical infrastructure, scraping issues, etc.), improve site quality, gain visibility and enhance your site’s interaction with Google.
What You Should Expect
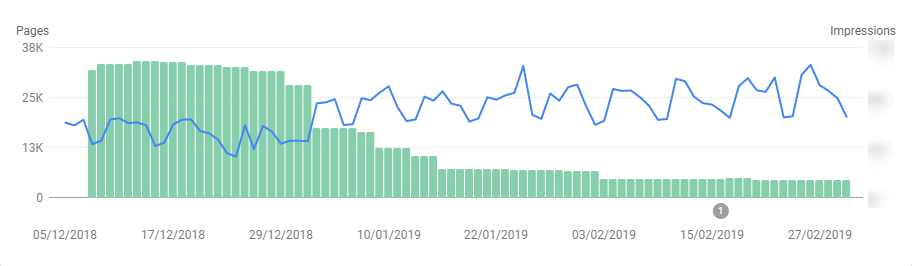
You should see the start of a trend. Listed below are the main expected changes:
Increase of traffic/visibility
An improved site in terms of crawled URLs. It’s now time to improve other aspects, such as content, ranking, conversion rate, brand, etc.
Slight decrease of traffic/visibility
This is to be expected, so plan for a small drop.
It should not largely affect your conversions.
Follow your overall SEO plan, and improve content accordingly (should be part of your improvement plan).
Same traffic/visibility
No real change in terms of visibility or traffic is a positive outcome as it highlights that the deleted pages meaning didn’t bring value.
This just means the overall health of the site has been improved.
In Conclusion
Deletion of low-value pages should be part of an overall SEO audit and undertaken with a structured plan for business improvements. After removal of the low-value content, every remaining page should have defined business goals: conversion, branding, support, traffic acquisition, etc.
Always ask the website owner for advice and feedback.
